Grapefruit in Combination with Medications can Cause Death
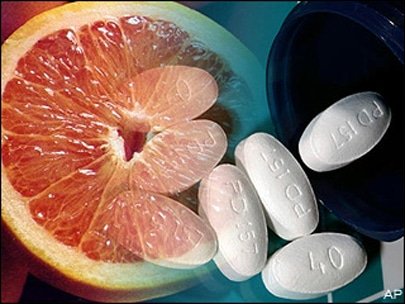 About 20 years ago, scientists first discovered that the adoption of some commonly used drugs in combination with conventional food may be dangerous to health. Due to chemical incompatibility may arise dangerous side effects, including death – anaphylactic shock, acute renal failure, respiratory failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, bone marrow suppression, and others.
About 20 years ago, scientists first discovered that the adoption of some commonly used drugs in combination with conventional food may be dangerous to health. Due to chemical incompatibility may arise dangerous side effects, including death – anaphylactic shock, acute renal failure, respiratory failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, bone marrow suppression, and others.
The staff of the Institute for the Study of the Lawson Health in London, Canada (Lawson Health Research Institute) explained the irreconcilability of medicine citrus, interaction of drugs with grapefruit and Seville orange. It was found that in these fruits are furanokumariny – active substances which are multiplied many times if the dose of the drug taken and making it deadly. According to specialists, a glass of orange juice a day can increase the dose of medication more than three times.
Scientists have determined that furanokumariny react with protein CYP3A4, which serves as a biochemical “trigger” for almost 50% of a certain type of medication. All incompatible furanokumarinami drugs have three characteristics: they are taken orally (swallowed) of the active substance in its entirety into the blood, and they always present CYP3A4, by which they are absorbed into the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
Says one of the authors of David Bailey,
With grapefruit do not mix a lot of drugs that are often prescribed for doctors, in the most ordinary cases, like cardiovascular disease. Likelihood of unpleasant effects increases as the last four years the number of incompatible medications with grapefruit grown .
According to the study, is to date 85 of these drugs, 43 of which cause death. Moreover, between 2008 and 2012, more medications are being sold that can cause serious side effects even death when combined with grapefruit juice. One of the common drugs that give an effect – simvastatin, based on which we have created dozens of drugs with different brand names.
Says Bailey,
If it is not written in the manual, physicians may not be aware of the incompatibility of drugs with citrus and warn the patient specifically. However, few patients give a full account of their diet, so can be a dangerous combination, unfortunately, a complete surprise to both.
The authors emphasize that furanokumariny remain in the body for hours after eating a grapefruit, so “suspicious” citrus during treatment safer to simply be excluded from the diet.
Via: cbsnews
Shortlink:

Recent Comments